Wood Sofa Frame Design: A Comprehensive Overview
The design of a wood sofa frame is a critical element in determining the overall aesthetics, durability, and comfort of a sofa. The frame provides the structural foundation upon which all other sofa components, such as the suspension system, cushioning, and upholstery, are built. A well-designed frame ensures longevity and prevents premature sagging or structural failure. This article explores the key considerations, design principles, and common materials used in wood sofa frame design.
Key Design Considerations
Several factors must be carefully considered when designing a wood sofa frame. These include the intended use of the sofa, the desired style, the weight it will need to support, and the overall dimensions. The design process should also incorporate considerations for manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
One of the primary considerations is the intended use. A sofa designed for heavy daily use in a family room will require a more robust frame than a sofa intended for occasional use in a guest room. This difference in usage affects the selection of wood species, the thicknesses of the frame members, and the types of joinery used.
The desired style of the sofa also significantly influences the frame design. A minimalist sofa with clean lines will require a different frame design than a more ornate, traditional sofa with curved elements. The frame must be designed to support the specific aesthetic features of the sofa. The style also affects the type of wood selected. Hardwoods are typically preferred for visible elements in higher-end sofas, while softer woods may be acceptable for internal, unseen components.
Weight-bearing capacity is a crucial aspect of frame design. The frame must be strong enough to support the weight of the cushions, upholstery, and the people using the sofa. Calculations must be made to determine the required strength of each frame member, taking into account factors such as the span of the members and the anticipated load distribution. The type and placement of support structures, like additional legs or internal bracing, also play a critical role in ensuring adequate weight-bearing capacity.
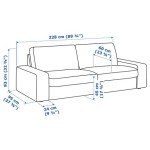
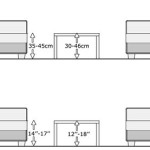
Finally, the overall dimensions of the sofa are a fundamental design parameter. The frame must be designed to precisely match the desired dimensions of the finished product. This includes not only the overall length, width, and height, but also the dimensions of the seat, back, and arms. Accuracy in these dimensions is crucial to ensure that the cushions and upholstery fit properly and that the sofa provides the desired level of comfort.
Common Wood Types and Their Properties
The selection of wood species for a sofa frame is a critical decision that directly impacts its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Hardwoods are generally preferred for their superior strength and resistance to wear and tear, but softwoods can also be used in certain applications where cost is a major concern or where less structural strength is required.
Hardwoods commonly used in sofa frame construction include oak, maple, birch, and ash. Oak is a popular choice due to its high strength, durability, and attractive grain pattern. It is well-suited for visible frame components. Maple offers similar strength characteristics and a finer grain, making it a good choice for a more modern aesthetic. Birch is another strong and relatively inexpensive hardwood that is often used in frame construction. Ash is valued for its flexibility and shock resistance, making it suitable for frames that need to withstand significant impact.
Softwoods, such as pine and fir, are less expensive than hardwoods but are also less strong and durable. They are often used for interior frame components or in sofas designed for light use. Pine is readily available and easy to work with, making it a popular choice for budget-friendly sofas. Fir is another softwood that can be used in frame construction, particularly in areas that are not subjected to high stress.
The choice of wood should also consider its moisture content. Wood that is too wet can warp or shrink as it dries, potentially compromising the structural integrity of the frame. Therefore, it is essential to use kiln-dried wood with a moisture content appropriate for the intended environment. This process helps to prevent dimensional changes and ensures that the frame remains stable over time.
Beyond the wood itself, the quality of the lumber is equally important. Select grade lumber, with minimal knots and imperfections, is generally preferred for sofa frame construction. This ensures a consistent level of strength and reduces the risk of structural failure.
Joinery Techniques for Wood Sofa Frames
The joinery techniques used to assemble a wood sofa frame are crucial for its structural integrity. Strong and durable joints are essential to prevent the frame from loosening or collapsing under load. Several different joinery techniques are commonly used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Mortise and tenon joints are among the strongest and most traditional types of wood joinery. A mortise is a hole cut into one piece of wood, and a tenon is a projecting piece on another piece of wood that fits into the mortise. The joint is often reinforced with glue and sometimes with pins or wedges. Mortise and tenon joints are particularly well-suited for connecting the legs of a sofa to the frame, as they provide excellent resistance to racking forces.
Dowel joints are another common type of wood joinery. Dowels are small cylindrical pieces of wood that are inserted into pre-drilled holes in the pieces being joined. Glue is used to secure the dowels in place. Dowel joints are relatively easy to create and can be used in a variety of applications, such as connecting frame members or attaching arms to the sofa body. While not as strong as mortise and tenon joints, dowel joints can provide adequate strength when properly designed and executed, especially when used in conjunction with other reinforcing elements.
Butt joints are the simplest type of wood joint, where two pieces of wood are simply butted together end-to-end or edge-to-edge. However, butt joints are inherently weak and require reinforcement to be suitable for sofa frame construction. Reinforcement can be achieved using screws, nails, glue, or metal brackets. Butt joints are often used in conjunction with other types of joinery to create more complex and stronger connections.
Miter joints are used to create angled connections, typically at corners. The pieces of wood are cut at an angle, usually 45 degrees, and then joined together to form a 90-degree corner. Miter joints are often used in the construction of sofa arms and backs. Like butt joints, miter joints are relatively weak and require reinforcement to be structurally sound. This can be achieved using splines, which are thin strips of wood that are inserted into slots cut into the mitered surfaces, or with metal fasteners.
In addition to the type of joinery used, the quality of the glue is also a critical factor in the overall strength of the frame. High-quality wood glue, such as polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue, is essential for creating strong and durable bonds between the wood pieces. The glue should be applied evenly and in sufficient quantity to ensure that all surfaces are properly bonded. Clamps should be used to hold the pieces together until the glue has fully cured.
Reinforcing elements, such as corner blocks and bracing, can be added to further strengthen the frame. Corner blocks are small pieces of wood that are attached to the inside corners of the frame, providing additional support and preventing racking. Bracing can be used to stiffen the frame and distribute loads more evenly. These reinforcing elements are particularly important in large or heavily used sofas.
Screw placement is another crucial aspect affecting joint strength. Screws should be of adequate length and thickness for the specific application. Pre-drilling pilot holes is generally recommended to prevent the wood from splitting when screws are inserted. The screws should be driven straight and deep enough to provide a secure hold.
The choice of joinery techniques should be based on a careful consideration of the intended use of the sofa, the type of wood being used, and the desired aesthetic. A well-designed and properly executed joinery system is essential for ensuring the long-term durability and stability of the sofa frame.
Ultimately, the design of a wood sofa frame is a complex process involving careful consideration of materials, construction techniques, and aesthetic considerations. A properly designed frame is the foundation of a comfortable, durable, and aesthetically pleasing sofa.

James Furniture Frames Built Sofa Wood Frame Wooden Designs

Low Seating Wooden Sofa With Solid Wood Frame A Sofá De Madeira Móveis Paletes Sofás Modernos

Comfortable Sofa With Wooden Frame Customizable Idfdesign

Solid Wooden Sofa Frame

Modern Brown Living Room 3 Seater Wooden Sofa Frame

Which Wood Type Is Perfect For Sofa Frames Just Furniture

How Much You Know About The Structure And Materials Of Modern Design Sofa Interi Furniture

James Furniture Frames Built Diy Chair Living Room Sofa Design Bed

Brown Wooden Sofa Frame Size 7x4 Ft

90 X 34 Size Polished Finish Modern Rectangular Shaped Wooden Sofa Frames At Best In New Delhi Ram Sundar Furniture